Understanding Joint Mobility
Joint mobility is about how well a joint can move through its range of motion without causing pain or harm. It’s a combination of flexibility and the movement capacity of the joint’s structures, including bones, muscles, tendons, and ligaments.
Effective joint mobility is crucial for performing daily activities comfortably and for maintaining overall health.
The Anatomy of Joints
To grasp joint mobility, it’s helpful to understand joint anatomy. Joints are the connections between bones that allow movement. At these junctions, cartilage covers the ends of the bones, providing a smooth, lubricated surface that reduces friction and absorbs shock.
Ligaments, which are tough bands of connective tissue, stabilize the joint by linking bones together, while tendons connect muscles to bones and help in movement by transmitting muscle force. The synovial fluid within the joint capsule, a fibrous envelope around the joint, further aids in lubrication and smooth movement.
How Joint Mobility Affects Overall Health
Good joint mobility has a significant impact on overall health. It allows for more efficient and smoother movement, which is essential for both everyday activities and physical performance. When joints move well, they can absorb shocks and adjust to sudden movements more effectively, reducing the risk of strains and sprains.
Proper mobility also supports better posture and alignment, which can minimize the risk of musculoskeletal issues and back pain. Additionally, regular movement and stretching, which enhance joint mobility, improve blood flow and metabolic processes, contributing to overall health.
Maintaining good joint mobility is also key for functional independence, helping individuals perform daily tasks such as bending, reaching, and walking with ease.
Common Issues Related to Poor Joint Mobility
When joint mobility is compromised, several problems can arise. Stiffness and pain are common, making movement difficult and uncomfortable. A reduced range of motion often accompanies poor mobility, leading to decreased flexibility and an increased risk of injury.
Chronic mobility issues can result in joint deformities or misalignments, such as those seen in arthritis. Muscle imbalances may develop, where some muscles become overused while others are underused, causing further complications.
Ultimately, poor joint mobility can affect daily activities, reduce physical activity levels, and impact mental well-being, leading to a lower quality of life.
Addressing joint mobility issues through appropriate exercises, stretching, and proper care can help mitigate these problems and support overall health.
If significant issues persist, consulting a healthcare professional or physical therapist is recommended for personalized guidance and treatment.
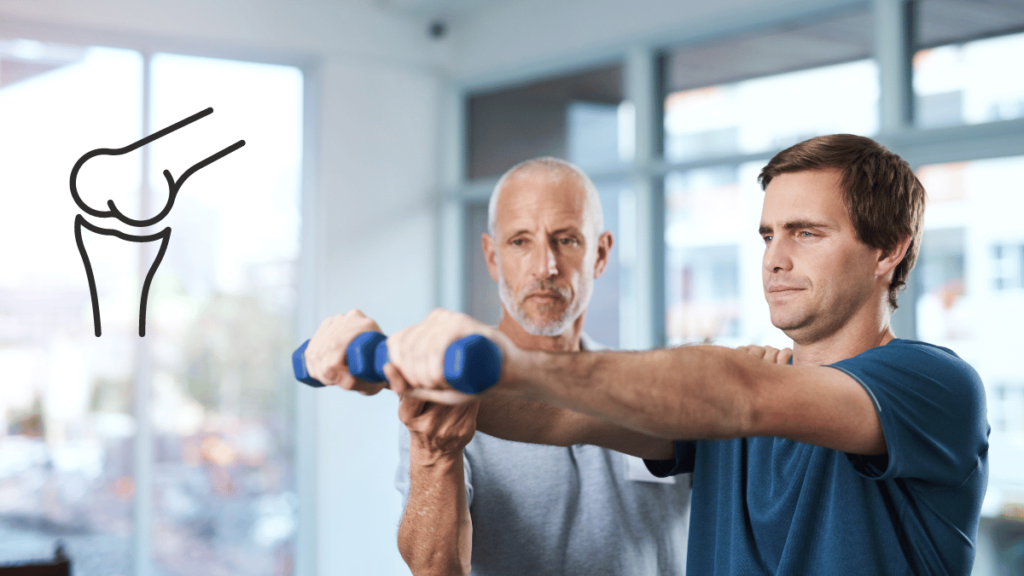

Benefits of Improved Joint Mobility
Improving joint mobility offers a range of benefits that can significantly enhance your quality of life. One of the primary advantages is enhanced flexibility and range of motion. When your joints move more freely, you can perform a wider variety of movements with ease, which is crucial for both daily activities and physical exercise.
This improved flexibility also reduces the risk of injury, as joints that move well can better absorb shocks and adapt to sudden movements, lowering the likelihood of strains and sprains.
Better joint mobility also contributes to improved athletic performance. Athletes with good joint mobility can execute their movements more efficiently and effectively, which can lead to better results and reduced fatigue.
Additionally, enhanced mobility supports better posture and balance, which are essential for both athletic performance and everyday activities. Proper alignment and balance help in maintaining a stable and efficient movement pattern, reducing the risk of falls and other accidents.
Exercises to Improve Joint Mobility
To enhance joint mobility, various exercises and routines can be incorporated into your daily or weekly fitness regimen.
Warm-Up Exercises: Starting with a warm-up is crucial as it prepares your body for more intense activity. Gentle movements like arm circles, leg swings, or light jogging increase blood flow to the muscles and joints, making them more pliable and ready for exercise.
Gentle Stretches: Gentle stretching helps lengthen muscles and improve joint flexibility. Incorporating stretches like hamstring stretches or shoulder rolls can enhance the range of motion and alleviate stiffness.
Light Cardio: Engaging in light cardio activities, such as brisk walking or cycling, promotes overall circulation and warms up the muscles and joints. This can improve flexibility and prepare your body for more focused mobility exercises.
Specific Joint Mobility Exercises: Targeted exercises for different joints are effective for improving mobility. For the shoulders, try shoulder rolls or arm circles. Hip mobility can be improved with exercises like hip circles or leg swings.
Knee and ankle mobility can benefit from exercises like knee hugs or ankle circles. These exercises help maintain and enhance the range of motion specific to each joint.
Dynamic vs. Static Stretching
Understanding the difference between dynamic and static stretching is important for effective mobility work. Dynamic stretching involves moving parts of your body through their full range of motion, like leg swings or torso twists. It’s often used as part of a warm-up to prepare muscles and joints for more strenuous activity.
Static stretching, on the other hand, involves holding a stretch for a prolonged period, usually between 15 to 60 seconds. It’s beneficial for improving flexibility and should be done after exercising to help with muscle recovery and reduce stiffness.
Tips for Maintaining Joint Mobility
Incorporating mobility work into your routine is key for long-term joint health. Aim to integrate mobility exercises regularly, ideally several times a week, to maintain flexibility and strength.
The role of nutrition is also crucial; a balanced diet rich in nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, which have anti-inflammatory properties, can support joint health. Staying hydrated is important as well, as fluids help maintain joint lubrication and overall function.
Avoiding common mistakes, such as overextending during stretches or neglecting to warm up, can prevent injuries and ensure more effective mobility work.
Joint Mobility and Aging
As we age, joint mobility often decreases due to factors like decreased collagen production, reduced muscle strength, and joint wear and tear. To counteract these changes, seniors can adopt strategies such as low-impact exercises, regular stretching, and strength training to maintain joint health and functionality.
Engaging in activities like swimming or yoga can be particularly beneficial due to their low-impact nature and focus on flexibility and balance.
Professional Help and Resources
If you encounter significant mobility issues or persistent pain, seeking professional help from a physical therapist can be invaluable. They can provide personalized assessments and tailored exercises to address specific needs. Additionally, various mobility tools and devices, such as foam rollers or resistance bands, can support your mobility routine.
There are also numerous useful apps and online resources that offer guided exercises, tips, and instructional videos to help you stay on track with your mobility goals.
Conclusion
In conclusion, maintaining and improving joint mobility is crucial for overall health and well-being. Enhanced joint mobility leads to greater flexibility and a wider range of motion, which can significantly reduce the risk of injury, enhance athletic performance, and support better posture and balance.
Incorporating a variety of exercises, such as warm-ups, gentle stretches, light cardio, and specific joint mobility drills, can effectively improve and maintain joint flexibility.
Understanding the roles of dynamic and static stretching and integrating these into your routine at the appropriate times can maximize benefits. Consistent mobility work, combined with a balanced diet, proper hydration, and avoidance of common mistakes, helps in sustaining joint health.
As we age, joint mobility naturally decreases, but adopting strategies like low-impact exercises and regular stretching can mitigate these changes. Seeking professional advice when needed and utilizing mobility tools and resources can further support your efforts.